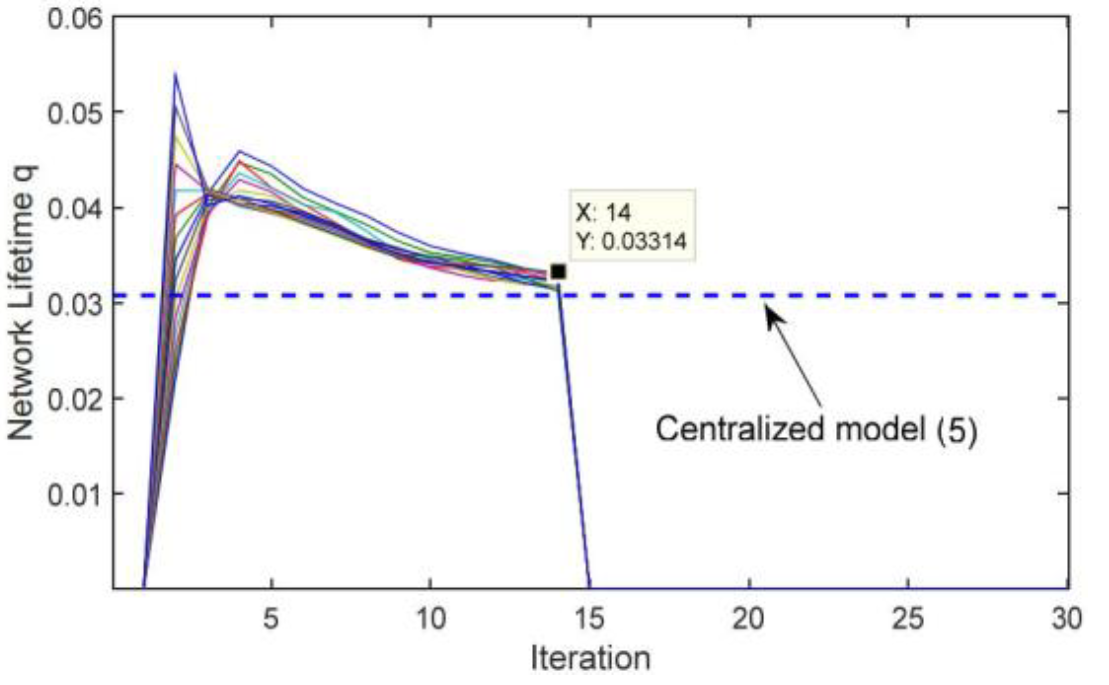
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) have the potential for realization economical automation systems in a smart grid where the different type of sensors mote can be used to monitor a wide range of the smart grid environment's parameters. Energy restriction of wireless sensor nodes and consequently lifetime of the network is a real challenge in WSNs applications like the smart grid. The WSN lifetime can be formulated as an optimization problem. In this paper, the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) algorithm is used to implement a novel distributed iterative algorithm for the problem of extending the sensor network lifetime. The proposed algorithm has some striking feature that including use of local information, low overhead of message passing, low computational complexity, fast convergence, and reduced energy consumption. The experiment results related to the convergence and number of iterations required to achieve the stopping criterion presented. As well as, the results of proposed algorithm compared with the subgradient methods. In comparison, the proposed ADMM-based algorithm outperforms the other methods.